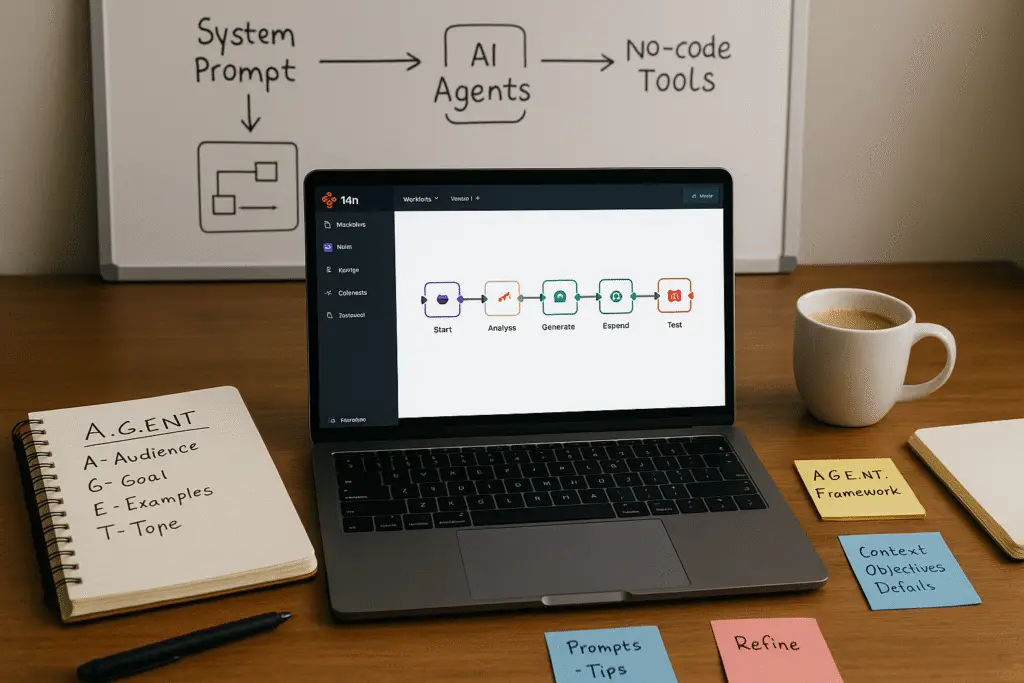
Introduction to the A.G.E.N.T. Framework
The A.G.E.N.T. framework is a pivotal tool designed for crafting effective AI system prompts, essential for anyone working with AI, from beginners to seasoned experts. Understanding this framework can significantly enhance your productivity and effectiveness in AI projects, enabling you to leverage AI tools to their fullest potential.
At its core, the A.G.E.N.T. framework is an acronym representing the key components necessary to create a system prompt that guides an AI agent effectively. The framework simplifies the process of defining how to communicate your needs clearly to the AI, ensuring consistent and valuable outputs. Let’s break down the components:

A – Ask
The first element of the framework is establishing your primary request from the AI agent, which should be articulated as a concise sentence. For instance, if you’re constructing a news agent, your ask might be to “Send me daily updates on AI tools.” This clarity at the onset makes it easier for the agent to understand its purpose.
G – Guidelines
Next, you outline the guidelines that the agent should adhere to when fulfilling your ask. These may include its role (e.g., being an expert researcher), tone of voice, the volume of output (e.g., how many articles to generate), and specific content requirements like word limits. This element ensures the AI’s responses align closely with your expectations, tailoring its behavior to suit your unique needs.
E – Examples
Providing both good and bad examples is crucial as it illustrates the specifics of what you do and do not want from the agent. For example, you might instruct your news agent to prioritize the latest updates on AI tools (good examples) while avoiding general trend analyses (bad examples). This guidance helps the AI learn the desired output nuances.
N – Notation
Defining the format in which the output should be presented is the next step, commonly utilizing JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). This format is preferred as it allows for easy data interchange between systems, making automation processes smoother and more efficient, especially in low-code environments like N8N.
T – Tools
Finally, identify the tools that your AI agent will have access to. This is akin to providing an intern with the necessary software to perform their duties effectively. Tools could include connections to databases, search engines like Perplexity, or collaboration software like Google Sheets. By providing these tools, you empower your agent to perform its tasks more effectively.
The importance of having a structured framework cannot be overstated. It not only ensures that no critical elements are overlooked but also enhances professional appearance, especially in client-facing roles, as it helps in conveying ideas and expectations in a polished manner.
Defining System Prompts: The Core of AI Agents
System prompts are foundational to the effective functioning of AI agents; they serve as the guiding instructions that define the role and purpose of the AI. To put it simply, a system prompt is akin to a mission statement for an AI agent: it dictates what the agent is meant to do and how it should execute those tasks. The clarity and structure of the system prompt directly influence the output quality and relevance, making its crafting crucial to achieving desired results.
The Importance of Frameworks in AI Agent Development
In order to craft impactful system prompts, a structured framework is beneficial. This framework consists of specific elements that every system prompt should contain to ensure the AI delivers outputs that align with user expectations. The acronym AGENT effectively summarizes these elements:
- Ask: This represents your primary request from the AI agent. It’s essential to articulate this in a clear, concise manner right at the beginning of your prompt. For instance, if you want the AI to provide daily news updates on AI tools, begin with that request explicitly stated.
- Guidelines: Here, you outline specific parameters that the AI should follow while generating responses. This could include defining the agent’s role (e.g., “expert researcher”), tone, the number of outputs required, word limits, and any other preferences tailored to your needs. The more tailored and explicit these guidelines are, the more aligned the AI’s output will be with your expectations.
- Examples: Providing both good and bad examples is crucial for the AI to discern the types of responses you desire. For example, if you want updates about significant AI tool launches, you might instruct the AI to avoid articles focused on predictions or trends that lack substance.
- Notation: Specifying how you want the output formatted is another best practice. A commonly preferred format is JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), which allows for clear structuring of the output. JSON is widely used in data interchange on the internet, making it practical for use in various applications and tools, including no-code automation platforms.
- Tools: Lastly, identify the tools the AI agent can access to achieve its tasks. For example, granting the AI access to external databases or online resources can expand its capabilities, helping to generate more comprehensive and accurate outputs.
An effective system prompt encapsulates these elements, leading to clearer, more actionable outputs. To illustrate the AGENT framework in practice, consider the example of an AI agent designed to send daily news updates. The agent’s system prompt might begin with a clear ask (e.g., “Summarize three impactful AI launches”), followed by detailed guidelines (e.g., “Use a professional tone, limit responses to 100 words, and exclude economic news”). Following this, good and bad examples of expected outputs can be provided, along with a JSON format for the output. Finally, the needed tools, such as a connection to news sources or a Google Sheet for tracking previously shared information, can be integrated.
By leveraging this structured approach to system prompts, AI builders can not only enhance performance and output quality but also ensure a more professional presentation of their AI solutions. As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, mastering the art of prompt crafting will be an invaluable skill for anyone seeking to harness the power of AI effectively.
Unpacking the A.G.E.N.T. Framework: Key Components
Structured frameworks play a pivotal role in the development of AI agents, providing a systematic way to build and enhance their functionality. At the core of this process is the concept of a system prompt, which encapsulates the agent’s purpose and directives. Well-structured prompts ensure that the AI comprehends its role, leading to desired outcomes in its responses.
Importance of Frameworks
Frameworks are vital for two primary reasons. First, they help prevent the omission of essential components when defining the specifications of an AI agent. This structured approach guarantees that every necessary aspect is addressed, ensuring the agent operates as expected. For instance, when constructing a news aggregation agent, details on the type of news (e.g., AI tools and updates), the desired tone, the number of articles, and the output format are articulated to create a cohesive operational framework.
Second, frameworks elevate professionalism, especially in client-facing roles. A well-organized structure conveys a sense of polish and clarity, fostering client trust and understanding. Clients are more likely to appreciate detailed frameworks, as they showcase thoughtfulness and a commitment to delivering quality outcomes.
Introduction to the AGENT Framework
The agent framework introduced here, known as AGENT, serves as an acronym for five key elements that every AI agent system prompt should include:
- Ask: Begin by clearly defining the primary request from the agent. This prompt informs the AI of its main objective. For example, if you’re creating an agent to fetch daily news on AI, your ask might be simply stated as “Provide daily updates on AI tools and advancements.”
- Guidelines: Specify the rules and expectations associated with the ask. This could cover aspects such as the tone of the agent, role specifications (like acting as an expert researcher), and output limitations, such as word count or article selection criteria.
- Examples: Provide the agent with good and bad examples to illustrate the desired output specifically. For instance, you can tell your news agent to prioritize breaking news articles, thereby excluding less relevant topics like general trends.
- Notation: Clearly define how the output should be structured. The best practice is to utilize JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), a widely accepted format for data exchange that aligns seamlessly with no-code automation tools, making it easier for integrations with services.
- Tools: Lastly, inform the agent about the tools available at its disposal, akin to the software you’d pre-install on a device for a new employee. Common tools might include access to Google Sheets for data logging or APIs for real-time browsing.
Practical Application: Building Your First AI Agent (News Robo)
To illustrate the efficacy of the AGENT framework, consider the example of a news-focused AI agent, termed ‘News Robo’. The framework elucidates how an intricate and professional output can stem from a simple configuration within a no-code automation platform like N8N. Once the agent is set up using the AGENT framework, executing it retrieves relevant news articles, organizes them, and formats them into a clear email report.
Moreover, the framework is versatile and can be adapted for various functionalities. For example, a meeting preparation agent can fetch a detailed background on a meeting participant, providing useful talking points. If the system prompt for such an agent is too broad, the results could be underwhelming; thus, refining the prompt using the AGENT framework makes outputs more relevant and actionable.
In a creative context, the framework proves beneficial as well. For instance, when creating a design agent for t-shirt graphics, clear specifications about design style, themes, and file formats using the AGENT framework ensure high-quality outputs that meet user expectations.
Conclusion
Investing time in learning how to implement structured frameworks like AGENT significantly streamlines the development of AI agents. With these best practices, settings can be established that ensure agents operate more effectively and professionally, making them invaluable tools across various domains. By integrating these elements into your AI setups, you not only enhance functionality but also elevate the user experience by delivering consistent and reliable outputs.
Enhancing AI Agents with Examples and Tools
The A.G.E.N.T. framework is a structured approach designed to create effective AI agents, enhancing their functionality and output reliability. Each element of this framework plays a significant role, and understanding its components—Ask, Guidelines, Examples, Notation, and Tools—will equip you with the knowledge necessary to implement AI agents effectively in your projects.
Ask
This is the starting point of the framework and arguably the most crucial element. Clearly articulating your primary request, or “ask,” ensures the AI agent knows precisely what is required of it. Typically, this is framed as a succinct, one-sentence request that guides the agent’s operations. For instance, if the agent is supposed to provide daily news updates about AI tools, stating this as the first point makes it clear what the agent’s primary focus should be.
Guidelines
Each agent comes with unique specifications, and the guidelines help define these parameters. This includes the agent’s role—whether it’s functioning as an expert researcher, the tone of voice it should use, how many articles to produce, and word limits for its output. These guidelines are flexible and can vary widely based on the task, which is why it’s beneficial to utilize tools that can suggest appropriate guidelines based on the ask.
Examples
Providing the AI agent with good and bad examples enhances its ability to understand the required output. Examples help clarify the types of responses expected and those that are not desired. For instance, in the context of a newsletter agent, you might specify that you want it to report on breaking news, like the release of GPT-5, while excluding speculative articles on trends or forecasts from sources like Forbes.
Notation
This element deals with the format in which outputs are generated. Establishing a clear structure, such as JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), is essential as it allows for the organization and transfer of information among different systems. JSON is especially effective for many AI applications because it enables easy data interchange and is compatible with numerous automation tools, such as N8N or Make.com.
Tools
Finally, the tools available to your AI agent are akin to the software pre-installed on an intern’s computer. These resources enhance the agent’s capabilities. For instance, an AI agent can be equipped with access to databases like Google Sheets, web browsing tools like Perplexity, or APIs that facilitate various functions. Providing these tools allows your AI agent to access and retrieve necessary information to perform its tasks effectively.
Exploring Additional AI Agent Examples
In this hands-on section, you will learn to develop your first AI agent, ‘News Robo,’ designed to automate the delivery of daily AI news updates. We’ll utilize the no-code tool N8N to create seamless workflows, making this process accessible even for beginners. By the end, you’ll have a functional AI application and a solid understanding of the A.G.E.N.T. framework, which stands for the essential components your system prompts should possess for effective AI behavior.
Creating ‘News Robo’
Now, let’s see how these concepts come together to create ‘News Robo.’ Here’s how to set it up in N8N:
- Execute the Agent: Launch N8N and set up a workflow that allows your AI agent to access the internet to gather news about AI tools. The AI will utilize OpenAI’s GPT model, functioning as its intelligence base.
- Configure the Agent Fields:
- User Prompt: You might use a simple command such as “research for me.”
- System Prompt: Here is where the A.G.E.N.T. framework comes into play. Define it as follows:
- *Ask*: “Summarize three impactful AI launches.”
- *Guidelines*: Limit each news item to a maximum of 100 words and exclude economic news stories that have been previously covered.
- *Examples*: Provide good examples of news sources to include and specify types of stories you want to avoid.
- *Notation*: Output format should be JSON.
- *Tools*: Include the Google Sheet for tracking past news items and the Perplexity tool for real-time internet access.
- Output Generation: Once configured, your agent will send daily email updates summarizing the latest news related to AI tools. This email will include sources and a brief explanation of why each news item is significant.
Example Outcomes
Through the application of the A.G.E.N.T. framework, your ‘News Robo’ agents should produce organized content that is both useful and easy to read. If setup correctly, each email sent out should deliver well-structured updates tailored to your preferences, ensuring you stay informed about the latest developments in AI.
Conclusion
Leveraging no-code frameworks like N8N, along with structured prompts from the A.G.E.N.T. model, empowers you to create capable AI agents with minimal technical expertise. Experiment with different asks, guidelines, examples, and tools to see what yields the best outputs for your specific needs. As you grow more familiar with this process, you can adapt the framework for a variety of applications, enhancing your productivity and engagement with AI technologies.
Leveraging GPT for Effortless System Prompts
Providing quality examples and useful tools is vital for enhancing your AI agent’s performance. The distinction between good and bad examples can profoundly influence your AI agent’s capability to understand tasks and produce relevant outputs. This difference comes down to clarity and context in the instructions given to the agent.
When creating an AI agent, quality examples act as a guide. They illustrate precisely what you want the agent to emulate and what to avoid. For instance, if you’re developing a newsletter AI agent to deliver breaking news about AI tools, a good example would specify that it should highlight significant milestones, such as the release of a major tool like GPT-5. Conversely, a bad example would involve broad or irrelevant topics, such as forecasts or trends that don’t directly inform the user about new tools. By providing both good and bad examples, you equip the AI with a clear understanding of how to navigate between ideal outputs and less desirable ones.
FAQs and Common Issues in AI Agent Setup
Additionally, practical tools like Google Sheets and Perplexity can significantly elevate your AI agent’s functionality. Using Google Sheets allows the agent to store and reference historical data, ensuring that it doesn’t repeat past outputs. For example, your newsletter AI agent can log previously covered news articles in a Google Sheet. The agent can check this sheet to cross-reference and avoid redundancy in the information it sends, thus maintaining the relevance and freshness of its updates.
Perplexity serves as another essential tool that enhances your AI agent’s responsiveness. It provides access to real-time information from the internet, allowing your agent to pull in current news and data that bolsters its responses. This capability is particularly useful for agents that need to stay ahead of trends and updates, as it broadens the range of content that the agent can include in its outputs.
Integrating these tools with a well-defined system prompt—such as those highlighted by the AGENT framework—ensures that your AI agent performs at its best. The framework emphasizes critical aspects:
- Ask: Define what you want the agent to do clearly.
- Guidelines: Establish rules and specifics about how to approach tasks, such as tone, output volume, and word count.
- Examples: Provide both positive and negative samples for reference.
- Notation: Outline the desired format for output, commonly in JSON, to ensure consistency and clarity.
- Tools: Specify which external resources the agent should access to enhance its performance.
By investing time to compose quality prompts and leveraging tools like Google Sheets and Perplexity, you elevate the responsiveness and utility of your AI agents, thus maximizing their effectiveness in delivering precise, relevant information tailored to user needs.
Tools Mentioned
The A.G.E.N.T. framework provides a structured way to build AI agents that can perform various tasks effectively. Below, we will explore three practical examples of AI agents: a Newsletter Robo, a Meeting Assistant, and a Creative Design Agent for shirt designs. Each example showcases the versatility of the A.G.E.N.T. framework and offers inspiration and templates you can use to initiate your own AI agent projects.
Newsletter Robo
The Newsletter Robo is an AI agent designed to send daily updates on a specific topic, such as AI tools and developments. The framework consists of properly defining the system prompt using the A.G.E.N.T. model:
- Ask: The agent is tasked with summarizing three impactful AI news articles each day.
- Guidelines: Set guidelines may include a maximum of 100 words per news item, exclusion of economic news, and a focus only on significant AI-related updates.
- Examples: The agent is provided with good examples of news topics it should cover, like updates on AI launches, while avoiding irrelevant topics like broad trend predictions.
- Notation: The output is structured in JSON format, which is advantageous as it is widely used for data interchange, especially in automation tools like N8N.
- Tools: The agent has access to tools such as Google Sheets for logging previously shared news articles to prevent duplication and Perplexity for browsing current news online.
When executed within the N8N environment, this agent pulls relevant articles using OpenAI’s GPT model, formats them according to the defined JSON structure, and sends a neat, organized email update.
Meeting Assistant
The Meeting Assistant is another straightforward but powerful AI agent. It provides background information about a person you are scheduled to meet, helping you prepare for calls or meetings.
- Ask: The agent’s primary job is to summarize key facts and talking points about the individual.
- Guidelines: The tone should be professional, and the output must be concise, maintaining a maximum character limit for each point.
- Examples: It’s essential to include examples of previously successful outputs, such as including a person’s recent activity or notable achievements.
- Notation: The summary should also conform to a JSON structure for better organization.
- Tools: It uses tools like Perplexity to gather information and can interact with messaging platforms like Slack for quick access.
Creative Design Agent for Shirt Designs
The Creative Design Agent focuses on creating shirt designs tailored for events and occasions. For instance, it might generate designs for Labor Day.
- Ask: The agent is required to create distinct shirt designs featuring engaging themes and texts relevant to upcoming events.
- Guidelines: Requirements may specify that designs should adhere to specific visual styles and maintain transparent backgrounds to simplify integrations with print-on-demand platforms.
- Examples: Good and bad design examples help clarify aesthetic goals for the AI.
- Notation: Outputs are defined in a straightforward JSON format to ensure structured and usable results.
- Tools: This agent utilizes tools like chat GPT for creative brainstorming and Dropbox for storing the finalized designs.
The system prompt, tailored through the A.G.E.N.T framework, empowers this agent to consistently generate quality designs, aiding users in capitalizing on merchandising opportunities.
In conclusion, these three examples illustrate the practical application of the A.G.E.N.T. framework in creating AI agents that serve diverse functions. By defining clear system prompts and leveraging tools effectively, you can build your own AI projects tailored to your unique needs.
To effectively leverage GPT models for generating and refining system prompts, it’s essential to understand the importance of a well-structured system prompt, which defines the purpose and role of your AI agent. A well-defined system prompt leads to better outputs. For instance, when creating a news aggregator AI agent, clearly stating that the agent should summarize impactful AI launches is crucial. This clarity allows the AI to understand its primary function from the outset.
The Importance of Frameworks in AI Agent Development
In order to craft impactful system prompts, a structured framework is beneficial. This framework consists of specific elements that every system prompt should contain to ensure the AI delivers outputs that align with user expectations. The acronym AGENT effectively summarizes these elements:
- Ask: This represents your primary request from the AI agent. It’s essential to articulate this in a clear, concise manner right at the beginning of your prompt. For instance, if you want the AI to provide daily news updates on AI tools, begin with that request explicitly stated.
- Guidelines: Here, you outline specific parameters that the AI should follow while generating responses. This could include defining the agent’s role (e.g., “expert researcher”), tone, the number of outputs required, word limits, and any other preferences tailored to your needs. The more tailored and explicit these guidelines are, the more aligned the AI’s output will be with your expectations.
- Examples: Providing both good and bad examples is crucial for the AI to discern the types of responses you desire. For example, if you want updates about significant AI tool launches, you might instruct the AI to avoid articles focused on predictions or trends that lack substance.
- Notation: Specifying how you want the output formatted is another best practice. A commonly preferred format is JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), which allows for clear structuring of the output. JSON is widely used in data interchange on the internet, making it practical for use in various applications and tools, including no-code automation platforms.
- Tools: Lastly, identify the tools the AI agent can access to achieve its tasks. For example, granting the AI access to external databases or online resources can expand its capabilities, helping to generate more comprehensive and accurate outputs.
An effective system prompt encapsulates these elements, leading to clearer, more actionable outputs. To illustrate the AGENT framework in practice, consider the example of an AI agent designed to send daily news updates. The agent’s system prompt might begin with a clear ask (e.g., “Summarize three impactful AI launches”), followed by detailed guidelines (e.g., “Use a professional tone, limit responses to 100 words, and exclude economic news”). Following this, good and bad examples of expected outputs can be provided, along with a JSON format for the output. Finally, the needed tools, such as a connection to news sources or a Google Sheet for tracking previously shared information, can be integrated.
By leveraging this structured approach to system prompts, AI builders can not only enhance performance and output quality but also ensure a more professional presentation of their AI solutions. As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, mastering the art of prompt crafting will be an invaluable skill for anyone seeking to harness the power of AI effectively.
Unpacking the A.G.E.N.T. Framework: Key Components
Structured frameworks play a pivotal role in the development of AI agents, providing a systematic way to build and enhance their functionality. At the core of this process is the concept of a system prompt, which encapsulates the agent’s purpose and directives. Well-structured prompts ensure that the AI comprehends its role, leading to desired outcomes in its responses.
Importance of Frameworks
Frameworks are vital for two primary reasons. First, they help prevent the omission of essential components when defining the specifications of an AI agent. This structured approach guarantees that every necessary aspect is addressed, ensuring the agent operates as expected. For instance, when constructing a news aggregation agent, details on the type of news (e.g., AI tools and updates), the desired tone, the number of articles, and the output format are articulated to create a cohesive operational framework.
Second, frameworks elevate professionalism, especially in client-facing roles. A well-organized structure conveys a sense of polish and clarity, fostering client trust and understanding. Clients are more likely to appreciate detailed frameworks, as they showcase thoughtfulness and a commitment to delivering quality outcomes.
Introduction to the AGENT Framework
The agent framework introduced here, known as AGENT, serves as an acronym for five key elements that every AI agent system prompt should include:
- Ask: Begin by clearly defining the primary request from the agent. This prompt informs the AI of its main objective. For example, if you’re creating an agent to fetch daily news on AI, your ask might be simply stated as “Provide daily updates on AI tools and advancements.”
- Guidelines: Specify the rules and expectations associated with the ask. This could cover aspects such as the tone of the agent, role specifications (like acting as an expert researcher), and output limitations, such as word count or article selection criteria.
- Examples: Provide the agent with good and bad examples to illustrate the desired output specifically. For instance, you can tell your news agent to prioritize breaking news articles, thereby excluding less relevant topics like general trends.
- Notation: Clearly define how the output should be structured. The best practice is to utilize JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), a widely accepted format for data exchange that aligns seamlessly with no-code automation tools, making it easier for integrations with services.
- Tools: Lastly, inform the agent about the tools available at its disposal, akin to the software you’d pre-install on a device for a new employee. Common tools might include access to Google Sheets for data logging or APIs for real-time browsing.
Practical Application: Building Your First AI Agent (News Robo)
To illustrate the efficacy of the AGENT framework, consider the example of a news-focused AI agent, termed ‘News Robo’. The framework elucidates how an intricate and professional output can stem from a simple configuration within a no-code automation platform like N8N. Once the agent is set up using the AGENT framework, executing it retrieves relevant news articles, organizes them, and formats them into a clear email report.
Moreover, the framework is versatile and can be adapted for various functionalities. For example, a meeting preparation agent can fetch a detailed background on a meeting participant, providing useful talking points. If the system prompt for such an agent is too broad, the results could be underwhelming; thus, refining the prompt using the AGENT framework makes outputs more relevant and actionable.
In a creative context, the framework proves beneficial as well. For instance, when creating a design agent for t-shirt graphics, clear specifications about design style, themes, and file formats using the AGENT framework ensure high-quality outputs that meet user expectations.
Conclusion
Investing time in learning how to implement structured frameworks like AGENT significantly streamlines the development of AI agents. With these best practices, settings can be established that ensure agents operate more effectively and professionally, making them invaluable tools across various domains. By integrating these elements into your AI setups, you not only enhance functionality but also elevate the user experience by delivering consistent and reliable outputs.
Enhancing AI Agents with Examples and Tools
The A.G.E.N.T. framework is a structured approach designed to create effective AI agents, enhancing their functionality and output reliability. Each element of this framework plays a significant role, and understanding its components—Ask, Guidelines, Examples, Notation, and Tools—will equip you with the knowledge necessary to implement AI agents effectively in your projects.
Ask
This is the starting point of the framework and arguably the most crucial element. Clearly articulating your primary request, or “ask,” ensures the AI agent knows precisely what is required of it. Typically, this is framed as a succinct, one-sentence request that guides the agent’s operations. For instance, if the agent is supposed to provide daily news updates about AI tools, stating this as the first point makes it clear what the agent’s primary focus should be.
Guidelines
Each agent comes with unique specifications, and the guidelines help define these parameters. This includes the agent’s role—whether it’s functioning as an expert researcher, the tone of voice it should use, how many articles to produce, and word limits for its output. These guidelines are flexible and can vary widely based on the task, which is why it’s beneficial to utilize tools that can suggest appropriate guidelines based on the ask.
Examples
Providing the AI agent with good and bad examples enhances its ability to understand the required output. Examples help clarify the types of responses expected and those that are not desired. For instance, in the context of a newsletter agent, you might specify that you want it to report on breaking news, like the release of GPT-5, while excluding speculative articles on trends or forecasts from sources like Forbes.
Notation
This element deals with the format in which outputs are generated. Establishing a clear structure, such as JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), is essential as it allows for the organization and transfer of information among different systems. JSON is especially effective for many AI applications because it enables easy data interchange and is compatible with numerous automation tools, such as N8N or Make.com.
Tools
Finally, the tools available to your AI agent are akin to the software pre-installed on an intern’s computer. These resources enhance the agent’s capabilities. For instance, an AI agent can be equipped with access to databases like Google Sheets, web browsing tools like Perplexity, or APIs that facilitate various functions. Providing these tools allows your AI agent to access and retrieve necessary information to perform its tasks effectively.
Exploring Additional AI Agent Examples
In this hands-on section, you will learn to develop your first AI agent, ‘News Robo,’ designed to automate the delivery of daily AI news updates. We’ll utilize the no-code tool N8N to create seamless workflows, making this process accessible even for beginners. By the end, you’ll have a functional AI application and a solid understanding of the A.G.E.N.T. framework, which stands for the essential components your system prompts should possess for effective AI behavior.
Creating ‘News Robo’
Now, let’s see how these concepts come together to create ‘News Robo.’ Here’s how to set it up in N8N:
- Execute the Agent: Launch N8N and set up a workflow that allows your AI agent to access the internet to gather news about AI tools. The AI will utilize OpenAI’s GPT model, functioning as its intelligence base.
- Configure the Agent Fields:
- User Prompt: You might use a simple command such as “research for me.”
- System Prompt: Here is where the A.G.E.N.T. framework comes into play. Define it as follows:
- *Ask*: “Summarize three impactful AI launches.”
- *Guidelines*: Limit each news item to a maximum of 100 words and exclude economic news stories that have been previously covered.
- *Examples*: Provide good examples of news sources to include and specify types of stories you want to avoid.
- *Notation*: Output format should be JSON.
- *Tools*: Include the Google Sheet for tracking past news items and the Perplexity tool for real-time internet access.
- Output Generation: Once configured, your agent will send daily email updates summarizing the latest news related to AI tools. This email will include sources and a brief explanation of why each news item is significant.
Example Outcomes
Through the application of the A.G.E.N.T. framework, your ‘News Robo’ agents should produce organized content that is both useful and easy to read. If setup correctly, each email sent out should deliver well-structured updates tailored to your preferences, ensuring you stay informed about the latest developments in AI.
Conclusion
Leveraging no-code frameworks like N8N, along with structured prompts from the A.G.E.N.T. model, empowers you to create capable AI agents with minimal technical expertise. Experiment with different asks, guidelines, examples, and tools to see what yields the best outputs for your specific needs. As you grow more familiar with this process, you can adapt the framework for a variety of applications, enhancing your productivity and engagement with AI technologies.
Leveraging GPT for Effortless System Prompts
Providing quality examples and useful tools is vital for enhancing your AI agent’s performance. The distinction between good and bad examples can profoundly influence your AI agent’s capability to understand tasks and produce relevant outputs. This difference comes down to clarity and context in the instructions given to the agent.
When creating an AI agent, quality examples act as a guide. They illustrate precisely what you want the agent to emulate and what to avoid. For instance, if you’re developing a newsletter AI agent to deliver breaking news about AI tools, a good example would specify that it should highlight significant milestones, such as the release of a major tool like GPT-5. Conversely, a bad example would involve broad or irrelevant topics, such as forecasts or trends that don’t directly inform the user about new tools. By providing both good and bad examples, you equip the AI with a clear understanding of how to navigate between ideal outputs and less desirable ones.
FAQs and Common Issues in AI Agent Setup
Additionally, practical tools like Google Sheets and Perplexity can significantly elevate your AI agent’s functionality. Using Google Sheets allows the agent to store and reference historical data, ensuring that it doesn’t repeat past outputs. For example, your newsletter AI agent can log previously covered news articles in a Google Sheet. The agent can check this sheet to cross-reference and avoid redundancy in the information it sends, thus maintaining the relevance and freshness of its updates.
Perplexity serves as another essential tool that enhances your AI agent’s responsiveness. It provides access to real-time information from the internet, allowing your agent to pull in current news and data that bolsters its responses. This capability is particularly useful for agents that need to stay ahead of trends and updates, as it broadens the range of content that the agent can include in its outputs.
Integrating these tools with a well-defined system prompt—such as those highlighted by the AGENT Framework—ensures that your AI agent performs at its best. The framework emphasizes critical aspects:
- Ask: Define what you want the agent to do clearly.
- Guidelines: Establish rules and specifics about how to approach tasks, such as tone, output volume, and word count.
- Examples: Provide both positive and negative samples for reference.
- Notation: Outline the desired format for output, commonly in JSON, to ensure consistency and clarity.
- Tools: Specify which external resources the agent should access to enhance its performance.
By investing time to compose quality prompts and leveraging tools like Google Sheets and Perplexity, you elevate the responsiveness and utility of your AI agents, thus maximizing their effectiveness in delivering precise, relevant information tailored to user needs.
Tools Mentioned
The A.G.E.N.T. framework provides a structured way to build AI agents that can perform various tasks effectively. Below, we will explore three practical examples of AI agents: a Newsletter Robo, a Meeting Assistant, and a Creative Design Agent for shirt designs. Each example showcases the versatility of the A.G.E.N.T. framework and offers inspiration and templates you can use to initiate your own AI agent projects.
Newsletter Robo
The Newsletter Robo is an AI agent designed to send daily updates on a specific topic, such as AI tools and developments. The framework consists of properly defining the system prompt using the A.G.E.N.T. model:
- Ask: The agent is tasked with summarizing three impactful AI news articles each day.
- Guidelines: Set guidelines may include a maximum of 100 words per news item, exclusion of economic news, and a focus only on significant AI-related updates.
- Examples: The agent is provided with good examples of news topics it should cover, like updates on AI launches, while avoiding irrelevant topics like broad trend predictions.
- Notation: The output is structured in JSON format, which is advantageous as it is widely used for data interchange, especially in automation tools like N8N.
- Tools: The agent has access to tools such as Google Sheets for logging previously shared news articles to prevent duplication and Perplexity for browsing current news online.
When executed within the N8N environment, this agent pulls relevant articles using OpenAI’s GPT model, formats them according to the defined JSON structure, and sends a neat, organized email update.
Meeting Assistant
The Meeting Assistant is another straightforward but powerful AI agent. It provides background information about a person you are scheduled to meet, helping you prepare for calls or meetings.
- Ask: The agent’s primary job is to summarize key facts and talking points about the individual.
- Guidelines: The tone should be professional, and the output must be concise, maintaining a maximum character limit for each point.
- Examples: It’s essential to include examples of previously successful outputs, such as including a person’s recent activity or notable achievements.
- Notation: The summary should also conform to a JSON structure for better organization.
- Tools: It uses tools like Perplexity to gather information and can interact with messaging platforms like Slack for quick access.
Creative Design Agent for Shirt Designs
The Creative Design Agent focuses on creating shirt designs tailored for events and occasions. For instance, it might generate designs for Labor Day.
- Ask: The agent is required to create distinct shirt designs featuring engaging themes and texts relevant to upcoming events.
- Guidelines: Requirements may specify that designs should adhere to specific visual styles and maintain transparent backgrounds to simplify integrations with print-on-demand platforms.
- Examples: Good and bad design examples help clarify aesthetic goals for the AI.
- Notation: Outputs are defined in a straightforward JSON format to ensure structured and usable results.
- Tools: This agent utilizes tools like chat GPT for creative brainstorming and Dropbox for storing the finalized designs.
The system prompt, tailored through the A.G.E.N.T framework, empowers this agent to consistently generate quality designs, aiding users in capitalizing on merchandising opportunities.
In conclusion, these three examples illustrate the practical application of the A.G.E.N.T. framework in creating AI agents that serve diverse functions. By defining clear system prompts and leveraging tools effectively, you can build your own AI projects tailored to your unique needs.
To effectively leverage GPT models for generating and refining system prompts, it’s essential to understand the importance of a well-structured system prompt, which defines the purpose and role of your AI agent. A well-defined system prompt leads to better outputs. For instance, when creating a news aggregator AI agent, clearly stating that the agent should summarize impactful AI launches is crucial. This clarity allows the AI to understand its primary function from the outset.